Unleashing the power of Data: Undercurrents and their Impact on Source Systems
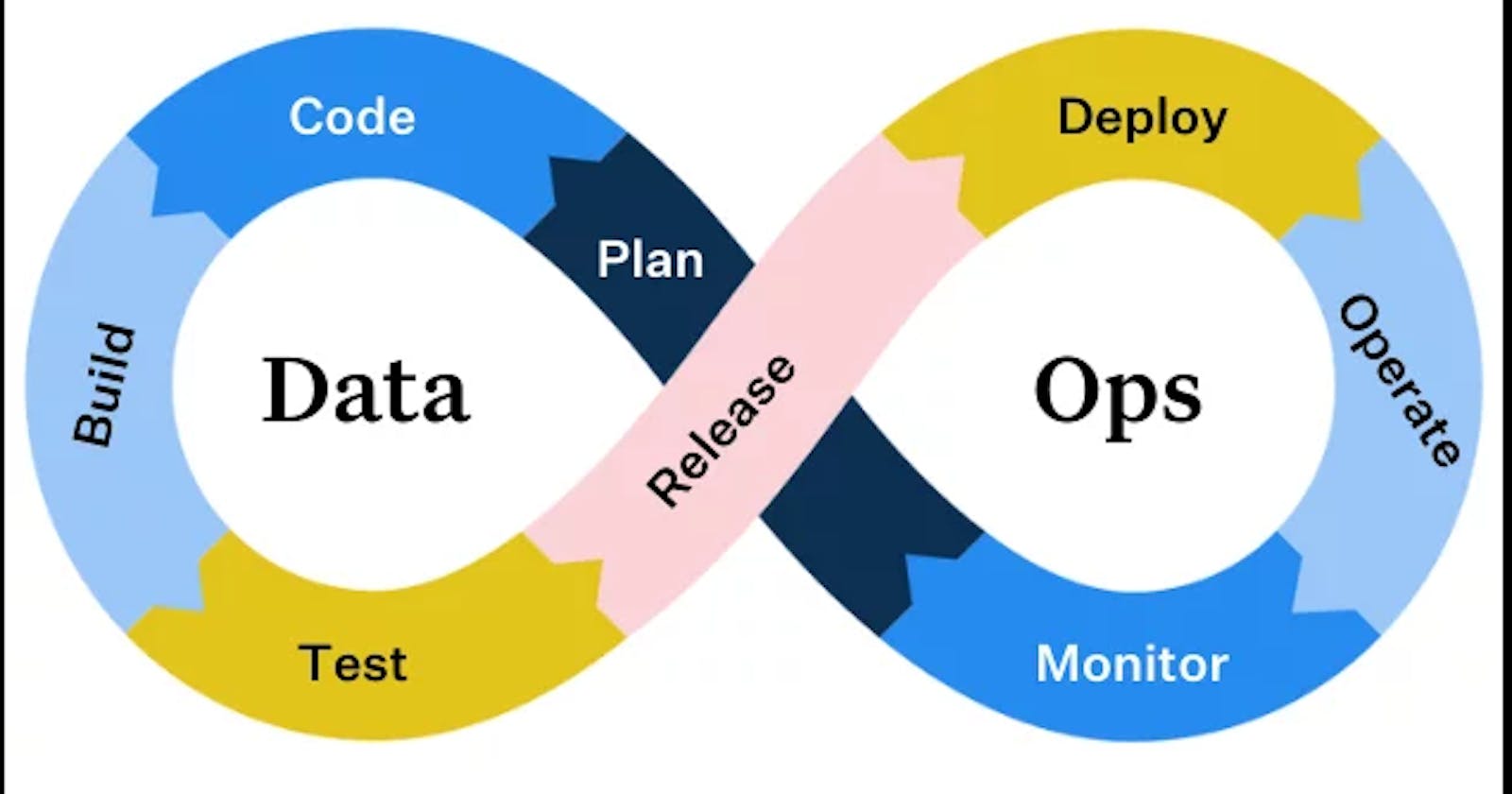
Data Engineering Lifecycle Indepth
Introduction
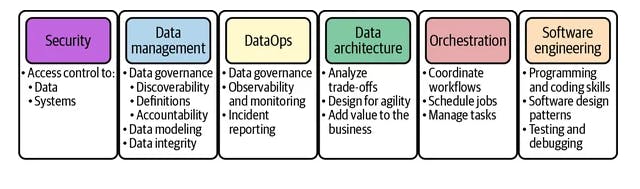
Welcome to another edition of our blog series on generation systems, where we delve into the fascinating world of data engineering and the critical role of source systems in this process. As data engineers, we understand that source systems are often beyond our direct control. We rely on stakeholders and system owners to follow best practices in data management, DataOps, data architecture, and software engineering. However, it is crucial to recognize the undercurrents at play within source systems and how they can significantly impact the data engineering lifecycle. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of these undercurrents and their implications for source systems. By addressing security, data management, DataOps, data architecture, orchestration, and software engineering, we can navigate the complexities of source systems and optimize the data engineering journey.
Security: Protecting the Data Fortress
In the realm of data engineering, security is of paramount importance. When dealing with source systems, it becomes crucial to establish robust security measures to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of data. This includes ensuring that data is securely encrypted both at rest and during transmission. Additionally, accessing source systems over public networks can introduce vulnerabilities, making it imperative to establish secure connections through virtual private networks (VPNs). Properly managing passwords, tokens, and credentials is also vital to preventing unauthorized access. Employing key management systems for secure storage of SSH keys and using password managers or single sign-on (SSO) providers for password storage are recommended practices. Furthermore, it is essential to establish trust in the source system's legitimacy to avoid data contamination from malicious actors. Implementing stringent security measures in source systems not only safeguards the data but also promotes trust and reliability in the overall data engineering process.
Data Management: Navigating the Upstream Challenges
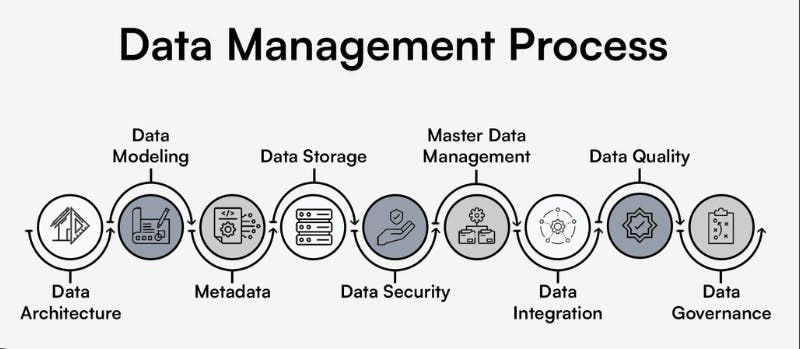
Data management within source systems presents unique challenges for data engineers, as they often have limited control over these systems. To ensure the smooth flow of data, it is crucial to understand how data is managed in source systems and how it influences data ingestion, storage, and transformation processes. Data governance plays a vital role in establishing reliable and easy-to-understand upstream data and system management practices. Collaborating with source system teams helps set expectations and establish effective communication channels for data quality assurance and integrity. Schema changes are an inevitable part of evolving source systems, and being notified of these changes in advance allows data engineers to adapt their pipelines accordingly. Master data management practices or systems that control the creation of upstream records can contribute to data consistency and integrity. Privacy and ethics considerations are also essential, including data obfuscation, retention policies, and compliance with regulatory requirements. By actively addressing these data management challenges, data engineers can ensure the reliability and quality of the data flowing through the source systems.
DataOps: Aligning Operational Excellence
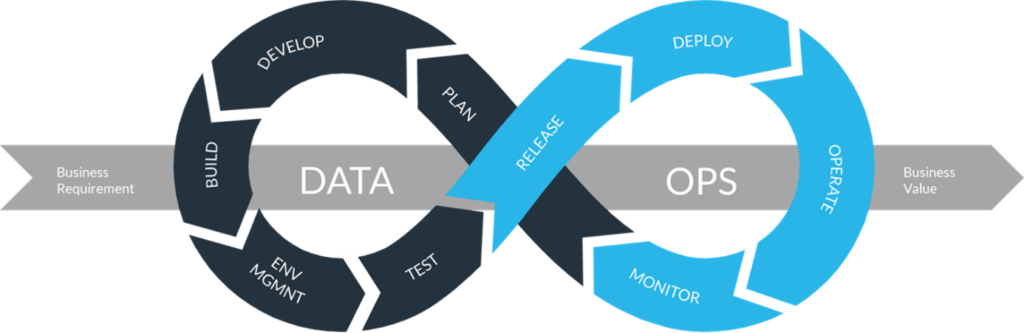
Operational excellence, encompassing practices such as DevOps and DataOps, plays a crucial role in the data engineering journey. While data engineers depend on stakeholders who control the source systems, establishing observability and monitoring mechanisms for source system uptime and usage is vital. This allows data engineers to promptly respond to incidents and minimize errors. Establishing clear communication channels between data engineering and the teams supporting the source systems is crucial. Ideally, these stakeholder teams have integrated DevOps practices into their workflow and culture, aligning their goals with DataOps principles. Automation is a key aspect of DataOps, enabling efficient source system updates and new feature implementations. However, it is essential to decouple the automation of the source system from the automation of data workflows to ensure independent operation. Observability plays a vital role in detecting and resolving issues, requiring robust monitoring of source system uptime and data quality. Additionally, incident response planning is crucial to mitigating the impact of source system failures on data pipelines. By incorporating DataOps principles into the data engineering process and establishing effective collaboration with source system teams, data engineers can enhance operational excellence and overall system reliability.
Data Architecture: Understanding the Foundations
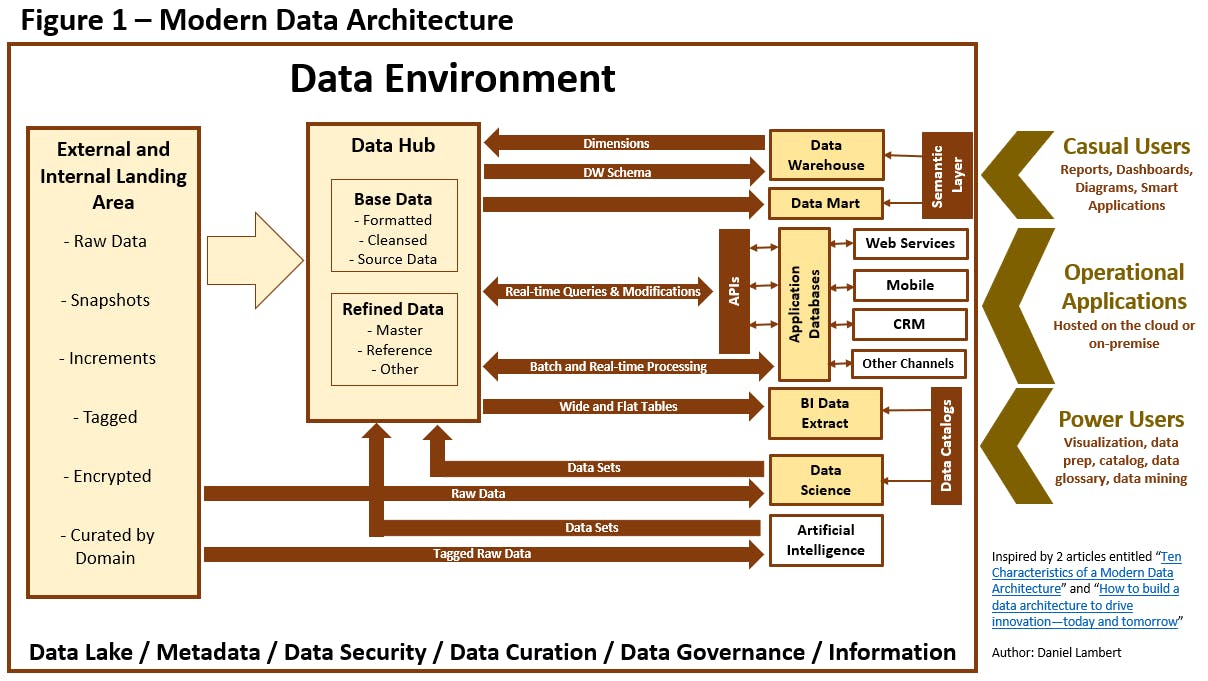
While data engineers may have limited control over source system architectures, understanding their design and characteristics is essential for efficient data engineering. Evaluating the reliability of the source system architecture is crucial, including considering factors such as system predictability and mean time to repair in case of failures. Durability is another critical aspect, as all systems are prone to failure. Therefore, understanding how the source system handles data loss during hardware failures or network outages is essential. Availability is another important consideration, ensuring that the source system is accessible when needed. Collaboration with the teams responsible for the source system architecture is crucial, as it allows data engineers to establish service level agreements (SLAs) and align their expectations with potential system failures. By gaining insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the source system architecture, data engineers can design robust and scalable data pipelines that leverage the existing infrastructure effectively.
Orchestration: Harmonizing Workflows

Orchestration plays a pivotal role in managing data engineering workflows and accessing source systems. Data engineers must ensure that their orchestration processes can seamlessly access the source systems, requiring proper network access, authentication, and authorization mechanisms. Understanding the cadence and frequency of data availability in the source system is crucial for planning data ingestion and processing. Integration of common frameworks, such as Kubernetes, can simplify the management of both application and data workloads. Collaboration between data engineers and application teams can help strike the right balance between integration and decoupling to minimize risks. Monitoring the performance and health of the source system through orchestration mechanisms allows data engineers to detect issues promptly. Implementing checks to ensure data quality and schema conformity during ingestion is essential for downstream usage. Additionally, establishing incident response plans to handle source system outages and efficiently backfill lost data is crucial to maintaining data pipeline integrity. By aligning orchestration practices with source system requirements, data engineers can optimize the overall data engineering workflow.
Software Engineering: Code as the Gateway
As data engineering increasingly involves writing code to access source systems, software engineering principles become integral to the process. Networking considerations are essential to ensure that the code can access the source system securely. Authentication and authorization mechanisms must be implemented to obtain the necessary credentials and IAM roles. Proper access pattern handling, whether through APIs or database drivers, requires thoughtful implementation, including retries, timeouts, and pagination strategies. Integration with orchestration frameworks allows code execution as part of orchestrated workflows. Parallelization techniques enable efficient and scalable access to source systems. Lastly, a robust deployment strategy ensures seamless integration of source code changes. By adhering to sound software engineering practices, data engineers can build reliable and scalable code for accessing source systems, enabling smooth data flows in the overall data engineering process.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have explored the undercurrents that shape the landscape of source systems and their profound impact on the data engineering journey. By addressing security concerns, understanding data management processes, embracing DataOps principles, evaluating source system architecture, optimizing orchestration, and employing robust software engineering practices, data engineers can navigate the complexities of source systems effectively. While source systems may lie beyond direct control, understanding their undercurrents empowers data engineers to build robust and reliable data pipelines, ensuring the availability, integrity, and usability of data for downstream processes. Through collaboration, communication, and continuous improvement, data engineers can harness the potential of source systems to unlock valuable insights and drive impactful data-driven solutions.