Mastering the basics: Powering Organizational Success
The Vital Role of Data Engineers
Introduction:
In the realm of data-driven organizations, data engineers play a crucial role in building and maintaining the data infrastructure that drives decision-making and business success. In this continuation of our blog series, we will explore the multifaceted nature of data engineers and their relationships with various roles within an organization. We will discuss the distinctions between internal and external facing data engineers, their contributions to organizational success, their collaborations with other technical roles, and their interactions with upstream and downstream stakeholders. Let's dive deeper into these essential aspects.
Upstream and Downstream Stakeholders:
Data engineers interact with both upstream and downstream stakeholders, forming integral connections in the data flow within an organization. Understanding these interactions is key to comprehending the full scope of a data engineer's responsibilities.
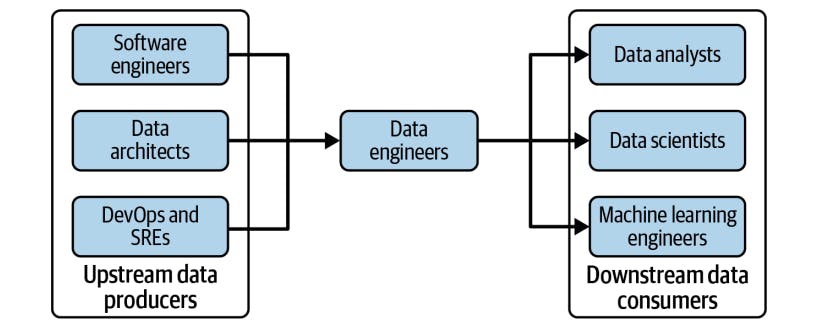
- Upstream Stakeholders:
Upstream stakeholders encompass the sources of incoming data, including internal data collection teams and external data vendors. Data engineers collaborate closely with these stakeholders to ensure the availability, quality, and seamless transmission of incoming data. By working in tandem with data providers, data engineers establish efficient data pipelines, perform comprehensive data validations, and address any issues related to data collection or transmission. These collaborations are critical in ensuring a continuous flow of high-quality data for downstream consumption and analysis.
- Downstream Stakeholders:
On the other end of the data flow, data engineers cater to downstream stakeholders who rely on accurate and reliable data for their analyses, reporting, and decision-making. These stakeholders may include data scientists, business analysts, and decision-makers. Data engineers collaborate with downstream stakeholders to understand their unique data requirements, implement data transformations to ensure data readiness and optimize data delivery mechanisms. By working closely with downstream stakeholders, data engineers empower them to extract valuable insights, generate meaningful reports, and make data-driven decisions that fuel organizational success.
Part 1: Internal-Facing Data Engineers

Internal-facing data engineers are at the core of constructing and maintaining the data infrastructure within an organization. Their responsibilities extend beyond data management to encompass designing robust data pipelines, ensuring data quality and reliability, and optimizing data storage and processing. Let's delve into their contributions and collaborations with various roles in more detail.
a. Collaboration with Data Scientists:
Data engineers closely collaborate with data scientists to bridge the gap between raw data and actionable insights. Together, they define data requirements, design data models, and implement data transformations. By partnering with data scientists, data engineers enable them to focus on analysis and modeling, confident that the necessary data is accessible and well-prepared. This collaboration facilitates the derivation of valuable insights from data, leading to informed decision-making and improved business outcomes.
b. Partnership with Business Analysts:
Business analysts heavily rely on data engineers to provide accurate and reliable data for reporting and decision-making. Data engineers collaborate with business analysts to understand their data needs, design data pipelines, and ensure data quality. Working hand in hand, they identify and address any data-related challenges, enabling business analysts to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions that drive organizational growth.
c. Integration with IT Teams:
Internal-facing data engineers closely collaborate with IT teams to set up and maintain the infrastructure required for data storage and processing. They work together to design scalable data storage systems, implement data warehouses and data lakes, and ensure data security. This collaboration ensures that data engineers receive the necessary support from IT teams to build and maintain a robust data infrastructure. The synergy between data engineers and IT teams allows for efficient data processing, storage, and retrieval, enabling the organization to effectively leverage its data assets.
Part 2: External Facing Data Engineers
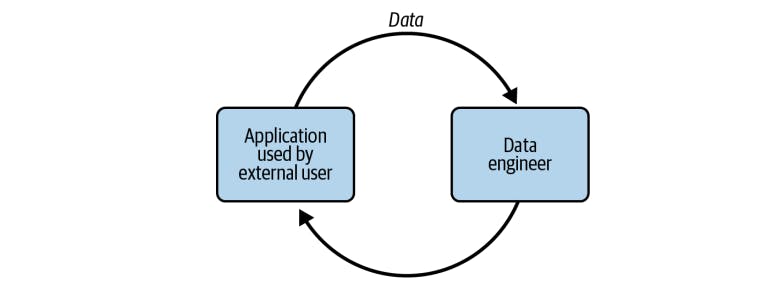
External-facing data engineers directly engage with external clients or stakeholders, providing data engineering solutions and support. They specialize in understanding client requirements, integrating data systems, and ensuring data security. Let's explore their contributions and collaborations in more detail.
a. Client Engagement and Solution Design:
External-facing data engineers work closely with clients to understand their unique data requirements and objectives. They play a pivotal role in designing data engineering solutions tailored to client needs, ensuring that data is collected, transformed, and delivered in a manner that aligns with client expectations. This collaboration requires a deep understanding of the client's industry, data ecosystem, and business objectives, allowing data engineers to provide customized solutions that meet specific client needs.
b. Data Integration and System Implementation:
External-facing data engineers excel in integrating data systems, whether it involves merging disparate data sources or implementing data pipelines between client systems. They leverage their technical expertise to ensure smooth data integration, enabling clients to access consolidated and reliable data for analysis and decision-making. This collaboration with external stakeholders requires strong communication skills and the ability to navigate complex data landscapes to deliver seamless data integration solutions.
c. Data Security and Compliance:
Data security is of utmost importance in today's digital landscape. External-facing data engineers collaborate with clients to ensure data security and compliance with industry regulations. They work closely with client IT teams and security experts to implement robust security measures, data encryption, and access controls. By prioritizing data security, external-facing data engineers instill confidence in clients, safeguard sensitive information, and maintain the integrity of data systems.
Conclusion:
Data engineers, whether internal or external facing, are instrumental in driving organizational success by building and maintaining the data infrastructure necessary for informed decision-making and business growth. Their collaborations with data scientists, business analysts, IT teams, clients, and other technical roles establish a seamless flow of data, enabling downstream stakeholders to derive valuable insights. By partnering with both upstream and downstream stakeholders, data engineers ensure the availability, quality, and reliability of data, paving the way for organizations to harness the full potential of their data assets.
I believe this comprehensive exploration of data engineers and their relationships with various roles within an organization has provided valuable insights. Stay tuned for the next part of our blog series, where we will delve into the impact of data engineers on business leadership and overall organizational strategy.
